Open banking is a financial service term that refers to a new era for the financial industry. It opens the door to innovations and serves consumers and their needs while maintaining a strong focus on security.
Open banking connects non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) and banks to provide customers with custom and more accessible financial services. Banking application programming interfaces (APIs) enable third-party developers to securely access customer financial data without compromising data compliance. Open banking also includes account aggregators that allow customers to manage all their banking accounts through a single platform.
APIs from banks also allow NBFCs to integrate banking functionality into their apps and services. This embedded banking enables NBFCs to verify customer information automatically, reducing the need for manual verification and accelerating customer verification. Moreover, open banking enables banking-as-a-service (BaaS) that allows banks to reach new customers through third parties and increase their revenue.
What is Open Banking?
In simple terms, open banking describes a practice of banks sharing various data with regulated third-party service providers. Banks provide access to consumer banking, transaction data and other financial information. This data is shared via secure Application Programming Interfaces (APIs).
The goal of open banking is to improve financial services for consumers. Opening up the data that legacy banks have historically kept in-house creates new opportunities. Open banking makes more space for new companies to step into the market and offer new, innovative products that benefit consumers.
It’s important to note that all the mentioned data is only shared once a customer chooses to share the information.
Opening the data creates different opportunities for involved parties:
- Fintech companies now have all the needed data and tools to create innovative products and services;
- Merchants can use the solutions offered by licensed financial service providers to improve their financial tools and payment flows; and
- Consumers enjoy more opportunities for spending, borrowing and investing their money.
How does Open Banking work?
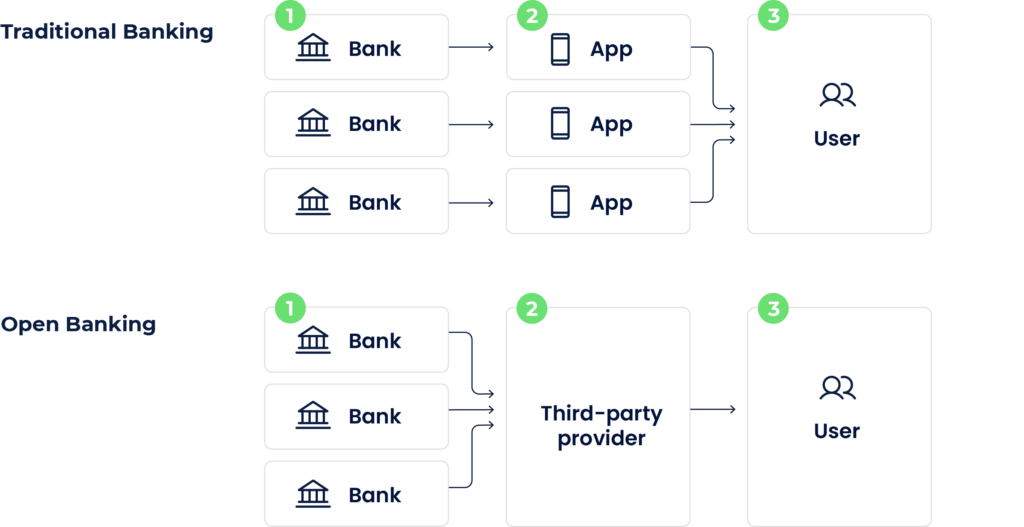
As mentioned, Open Banking uses APIs for data sharing. Before we move on to explain this data sharing, it’s important to understand how APIs work. In simple words, APIs are a way for software to communicate with other software and exchange information.
In Open Banking, banks give their APIs to authorised financial service providers. These APIs contain various pieces of information, such as an account holder’s name, account type, currency, transaction history, etc.
This information is only made available to the third-party service providers once the account holder explicitly agrees to share the data. Consumers usually give their consent via an online form by agreeing to terms and conditions.
Once the consumer agrees to share their data, the third-party service providers can access the relevant shared information via APIs. Building and implementing the APIs are up to banks.
What is an example of Open Banking?
Merchants and consumers already widely enjoy the benefits of Open Banking. Here are three of many examples of the new opportunities it has created:
1. Payment initiation service (PIS)
Thanks to Open Banking, companies can use payment initiation services to offer a better checkout experience to their customers. Online payment gateway service providers stepped into the market and remarkably improved the checkout flows.
For example, previously, consumers often had to pay for goods by making an online transfer from their bank account. To do this, they would have to open a number of different tabs, copy and paste or even type in account details to make the payment. Such a payment flow was inconvenient, risky and time-consuming.
With Open Banking, fintech companies have created convenient payment initiation services. These innovative solutions allow consumers to pay for goods securely with just a few clicks. Improved payment flows also increase sales, since fewer shoppers abandon their carts due to an inconvenient payment process.
2. Account information service (AIS)
Open Banking allows loan providers to access information from different banks quickly. In the past, if someone applied for a loan, the lender would have to gather large amounts of information about the person’s financial history. It would be a lengthy process to collect the data, and would require resources from all the parties involved: the lender, banks, and the applicant.
Banking APIs make the process much easier. The lender can digitally request information from the bank’s APIs and receive it in seconds with the applicant’s permission. The process becomes much faster and requires significantly fewer resources than before.
3. Fewer transaction fees
Consumers rarely think about the fees that merchants need to pay in order to accept card payments. Each card transaction can include up to 15 different fees, which can inflate the cost of goods and services.
To avoid these fees, merchants in physical stores sometimes have to make difficult decisions. Some shops would choose not to support card payments altogether. Others might set a minimum charge or ask consumers to pay extra for card payments. Online merchants would ask clients to make money transfers from their bank accounts, leading to a set of steps that were previously discussed.
Open Banking paved the way for account-to-account (A2A) payments that allow shoppers to pay for goods and services directly from their bank account. Consumers can even link their bank account to a merchant’s app or a web page and make payments in one click. Paying directly from bank accounts removes all the card processing fees and benefits both merchants and consumers.
Why do we need Open Banking?
For many years, banks have been some of the most legacy-burdened industries. While many people appreciate conservative approaches when it comes to finances, the situation has mostly benefited the largest banks and not the consumers. Previously, there was no place for innovations in the banking industry.
Open Banking is a breath of fresh air compared to legacy banking. It opens the door to much-needed innovations in the financial industry, and moves it out of stagnation. These are the main reasons why we need the new banking system:
- It creates more competition for banks and challenges them to offer better products and services for a better price;
- It shifts the focus from generating funds for banks to improving the customer experience; and
- The new way of banking allows more space for innovations and encourages companies to find solutions to long-running issues.
What are the benefits of Open Banking?
it has manny different benefits for both businesses or financial institutions and customers, but the main ones are
- Better customer experience;
- New revenue streams; and
- Sustainable service model.
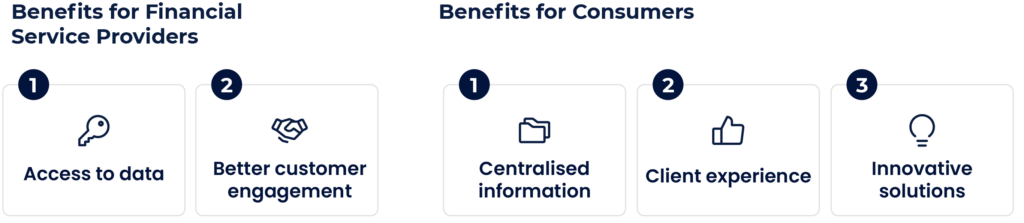
Benefits for businesses
Access to data — The new system has democratised the space that has been long-ruled by legacy banks. Fintechs and other companies can now access the same data as big banks, which creates fairer opportunities for businesses of all sizes. Even the smallest companies now have the tools to join the competition.
Better customer engagement — The data that open banking makes accessible allows businesses to provide personalised offerings to their customers. Analysing the data helps make relevant suggestions to different clients based on their financial habits, and this way increases client engagement.
Benefits for consumers
Centralised information — Open Banking made it possible to track financial information in one place. All data can be accessed via one app, allowing users to make informed decisions and deal with personal finances better. This way, consumers gain more control over their finances.
Client experience — Since the introduction of open banking, nearly every big bank has created a mobile app, digitalised a large part of their services and drastically reduced the waiting time for their clients. At the same time, fintechs have introduced various solutions that improve payment flows, make money borrowing easier and simplify investing.
Innovative solutions — Many solutions that have been developed thanks to the new banking system benefit consumers. Quicker checkout flows, easier mobile payments and digitalised banking services have been brought about by open banking. We can only imagine what great innovations are coming up next.
